Multimedia Authoring
Anna Luoma
NETWORKS - THEIR QUALITIES AND FUNCTIONS
€ topological and geometrical points of view
€ the network theories based on geometrical thinking: network is a system combined by nodes and connections between these nodes
€ "the Official Definition":
If we have a group of points (A, B, C...) and some of the pairs of the points are combined by lines , the configuration is called a network. The points which are connected with at least one other point are called nodes. The combining lines are called links
Information networks and computer networks
€ information network is a system, which is organised as a network and its purpose is to handle information
€ a system, which consists of computer hardware and software and transmits communication based on network traffic between two or more users regardless of time or space
€ interaction system or structure of different kinds of nodes
€ nodes: human beings, groups, institutions, machines, computers
€ nodes are operators of the networks
€ normally the term node refers to servers (hosts)
€ the broader meaning: data base, information service, community, person, or even another network (2 or more networks connected = internet)
€ normally the networks contribute a man-machine -mix
€ networks are organisational systems where interaction (connections or transmission of information) between the nodes is happening
€ --> networks are really communication systems
€ earlier networks were seen as horizontal correspondents to vertical hierarchies
€ in fact, networks are multi-dimensional, concepts horizontal/vertical are not valid
Physical and logical networks
€ physical network shows the topology formed by the links and the linked nodes
€ logical network means operations and operators, rules, security activities etc. which operate on the physical network
€ analogy: symphony orchestra performing: the orchestra would be the physical network and the performance (melodies, rhythm etc.) would represent the logical network
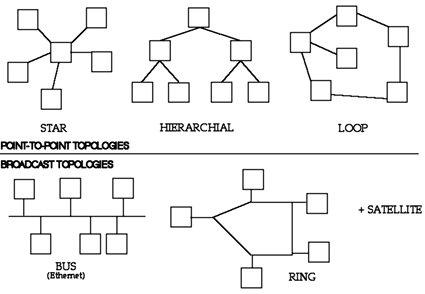
Topological point of view
€ star model --> tree --> snow crystal --> fish net etc.
€ star is a point-to-point topology
€ a bus model is a broadcast topology (Ethernet, token ring)
Routing
€ "host" - connected computer
€ "server" - processes or computers with resources to share
€ "client" - processes or computers that use resources. A software program that is used to contact and obtain from a server software program on another computer
€ "backbone " - the primary networks that form a major pathway within the broader network
€ modem - (MOdulator, DEModulator)
€ messages between computers are converted to small packets that are rapidly routed to their destinations (packet switching)
€ routers are used to forward packets in the appropriate direction
€ not all packets are sent out over the same route
€ routing depends on traffic loads and what backbone is working at the moment
€ bandwidth - the range of frequencies that can be passed from one end of the medium to the other. How much "stuff" you can send through a connection. Usually measured in bits-per-second
€ ASCII - (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) World-wide standard for the code numbers used by computers to represent all the letters, numbers, punctuation etc.
Protocol layers
€ information networks have protocol layers
- The International Standards Organization (ISO):
physical (cable size, connector etc.)
data link (low-level error detection)
network (routing packets)
transport (establishing connection)
session (keeps communication flowing)
presentation (conversion)
application (programs)
Each layer in a protocol system uses the previous layer or layers to take action
LANs and WANs
€ local area networks (LANs) for example an internal network of a company
€ wide area networks (WANs)
Requirement networks
€ in addition to technical construction, there is another side of network theory: requirement networks
€ combined by needs, desires, demands, targets, visions etc.
€ "from technology push to user pull!"
Human networks inside the organizations
€ earlier a typical model of organizational activities was hierarchy or pyramid, nowadays focus is on non-hierarchical network models
€ qualifications for human networks:
- agreed distribution of work
- proper use and compatibility of special skills
- confidence on individuals' skills and initiatives
- respect to other people's work
- equal rights
- commonly decided goals
- leadership seen as part of distribution of work, instead of principal/employee
- relationship
- no hierarchy structures
- continuous interaction
TECHNOLOGICAL BASIS OF NETWORKED ORGANIZATION
€ technical components provide the necessary infrastructure but by themselves do not create networked organization
€ first-level effects (efficiency) and second-level effects (social system)
€ the efficient uses of information networks in companies:
- e-mail (reduces the delays of telephone tag and snail mail)
- group postings (Does anybody know... messages, memos)
- joint projects with partners
- brainstorming, scheduling, task assignments
- reporting accomplishments
- general awareness
€ face-to-face meetings still needed
€ "intelprise" - a new form of collaborative organization, physically supported by groupmedia
€ "groupmedia" - a convergence of CMC and CSCV (computer-supported cooperative work)
€ problems: lack of authorities, changes in work manners
Information work - Working/studying from a distance
€ "telework"
€ consists of manipulation of information (text, images, sounds), is very independent and not time or space limited
€ James Robertson 1987: in future each one of us is either doing so called ownwork or is entrepreneur (owner of independent enterprise) or more probably an intrapreneur, who has an independent enterprise inside the bigger organization
€ the best candidates for telework are clerical employees and relatively autonomous professionals such as writers or designers
€ "networkplace" - the networld primarily devoted to work-related communication
€ "knowledge workers" - academics, scientists, students and researchers who use networks to collaborate with colleagues, access specific expertise, share information etc.
€ communication technology offers tools for promoting the global education of students AND teachers
€ "virtual classrooms"
€ "electronic learning circles"
€ "global campus"
COMPUTER MEDIATED COMMUNICATION
€ many-to-many communication
€ the new communication technology has opened new doors for human contact and new avenues for social, intellectual, economic and political growth
€ still: we should not be interacting with computers but through computers
€ people are not just looking for information but possibilities to communicate
€ Oldenburg 1991: there are three essential places in every person's life: the place they live, the place they work and the place they gather for conviviality
€ the connections between the people are now created regardless of time and place --> 24 hours communication
--> networks become places WHERE we communicate = networlds!
€ this place has a lot of names: the Net, the Web, the Cloud, the Matrix, the Datasphere, the Electronic Frontier, the information superhighway etc.
€ "anyplace communication" - transcends geographic barriers to enable people to access the people and resources they need
€ "anytime communication" - most networks are based on asynchronous, not real-time, communication (to overcome time zones and personal schedules) problem: possible lack of immediate feedback
€ group interactivity - online people can establish communication on the basis of shared interest, not merely shared geography --> new contacts
€ "in a traditional kinds of communities, we are accustomed to meeting people, then getting to know them; in virtual communities you can get to know people and then choose to meet them"
€ new skills needed: to reduce and encode your own identity as words on a screen and to decode and unpack the identities of others
€ computer mediation - text-based messaging
- direct while informal
- communication in the networld is "blind" to vertical hierarchy in social relationships
€ the ways in which people use CMC always should root in human needs, not hardware of software
€ the focus should not be on silicon but on the ways people need to, fail to, and try to communicate with one another
€ the increased communication of course expresses intercultural and cross-cultural differences
€ for example, different cultures provide different ways of decision making
€ convergence theory: if two or more individuals share information with one another, then over time they will tend to converge toward one another, leading to a state of greater uniformity
€ we have enough know-how, do we have know-why?
INFORMATION AS A PRODUCT
| Book | Computer File |
Difficult to produce,
slow, expensive to
circulate, needs a lot of
storing space | Easy to produce, quick,
cheap to circulate, does not
need much of storing space |
No compatibility
problems, does not
require electricity,
not exposed to viruses, easy
to read, you don't need
a manual to learn how
to use it | Compatibility problmes,
dependent on electricity,
exposed to viruses,
difficult to read,
manuals required
|
€ Networks carry information. Networks hide information.
€ information itself does not mean power, the information of existing information does!
€ computer mediated information is easily edited, copied and spread (even forwarded!), this mean huge change in the meaning and role of information
€ very important to know how to find the pieces of information, which may be located all over the networks - and some of the pieces user may have to create him/herself
€ then how to create the whole picture of the pieces of information found from the networks
€ from reactive thinking to proactive thinking
€ media literacy skills?
- "abilities to read and write together with the skills of using information and rebel!
€ "informatization" - the new wave of innovation in industrial technology
€ commercialization? (availability, social significance) information services sponsored by giant companies....
€ the truth value? (no more blacks and whites, only greys)
€ do people want information or entertainment?
The copyrights
€ EU extended the copyright protection into 70 years
€ how to find a way the users could use the images and the authors would get the payment
€ quotation rights like the textual material has
Information rights
€ information autonomy/security right
€ information title/priority right
€ information control/privacy right
Links
- ComserveInformation service provided by Communication Institute for Online Scholarship
- Imagologies(review) Authors: Mark C. Taylor and Esa Saarinen. This is a non-book for a virtual age. "Imagologies, as a critical and cultural investigation into the functioning and forms of production of the image technologies of our time, sets itself within the tradition that Foucault describes as a critical inquiry into ourselves."
- Imagologies (review)Authors: Mark C. Taylor and Esa Saarinen
 Back to index
Back to index
E-mail:anna.luoma@uwasa.fi

 Back to index
Back to index